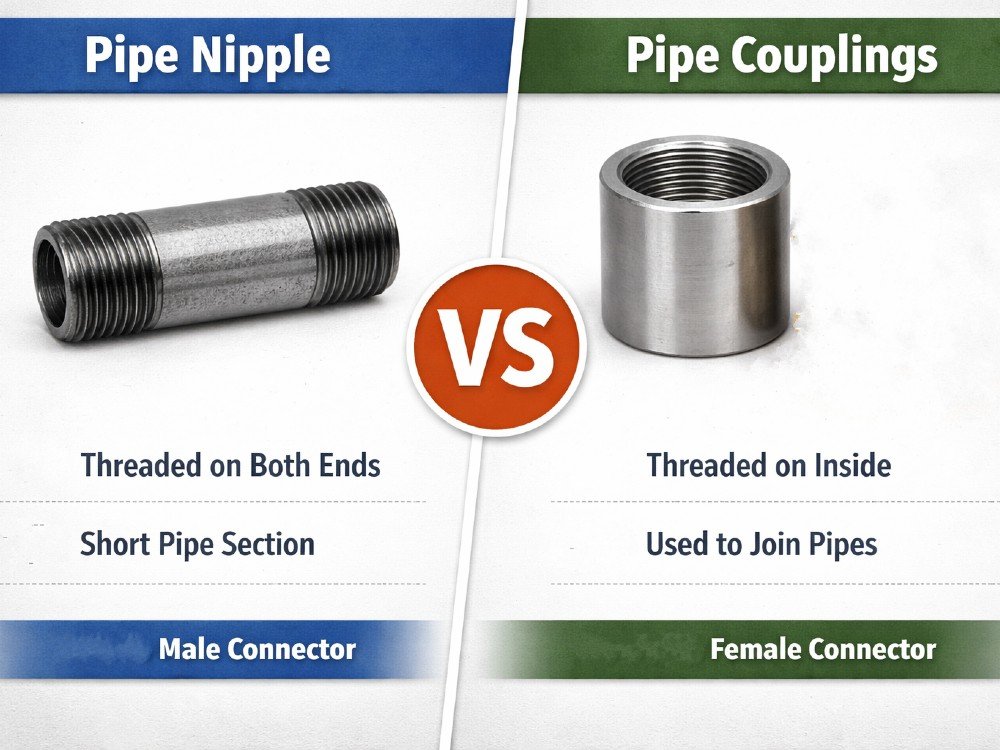
When specifying pipe fittings for your industrial project, understanding the fundamental differences between pipe nipples and pipe couplings is crucial. While both are essential threaded fittings, they serve distinctly different purposes in piping systems. This comprehensive guide will help you make informed decisions for your next project.↳
What is a Pipe Nipple?
A pipe nipple is a short length of pipe with male external threads on both ends. It’s one of the most common and versatile fittings in piping systems, used to extend pipes or connect two female-threaded fittings.
Key Characteristics of Pipe Nipples:
- External (male) threads on both ends
- Available in various lengths: From close nipples (minimal unthreaded section) to 12 inches or longer
- Straight pipe section with no internal components
- Thread types: NPT, BSP, DIN, BSPT
- Sizes: Typically 1/8″ to 6″ diameter
Types of Pipe Nipples:
- Close Nipple
- Threads run nearly end-to-end with minimal unthreaded center
- Used when minimum spacing is required
- Common in water meter installations
- Shoulder Nipple
- Short unthreaded section in the center
- Allows slight spacing between fittings
- Easier to grip during installation
- Barrel Nipple (Long Nipple)
- Significant unthreaded section in the middle
- Available in standard lengths (2″, 3″, 4″, 6″, 8″, 10″, 12″)
- Used for pipe extensions and longer connections
- Swage Nipple
- One end is larger diameter than the other
- Used for transitioning between different pipe sizes
- Less common than reducing couplings
Common Applications for Pipe Nipples:
✓ Connecting two female-threaded fittings (valves, couplings, elbows) ✓ Extending existing pipe runs ✓ Creating branch connections with tees ✓ Connecting fixtures to supply lines ✓ Manifold assemblies ✓ Gauge and instrument connections ✓ Water meter installations (close nipples)
What is a Pipe Coupling?
A pipe coupling is a short fitting with internal female threads on one or both ends, designed to join two pipes or fittings together.↳
Key Characteristics of Pipe Couplings:
- Internal (female) threads
- Shorter than most nipples
- Available in full, half, and reducing versions
- Cylindrical or hexagonal body shape
- No significant length extension to the system
Types of Pipe Couplings:
- Full Coupling (Standard Coupling)
- Female threads on both ends
- Connects two male-threaded pipes or nipples
- Same size threads on both ends
- Most common coupling type
- Half Coupling
- Female thread on one end only
- Socket weld or plain end on the other
- Used for branch connections
- Welded to pipe or vessel, threaded connection for valve/instrument
- Reducing Coupling
- Two different thread sizes
- Larger thread on one end, smaller on the other
- Transitions between pipe sizes
- Often hexagonal for wrench grip
Direct Comparison: Pipe Nipples vs Pipe Couplings
| Feature | Pipe Nipple | Pipe Coupling |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | External (male) both ends | Internal (female) one or both ends |
| Primary Function | Connect female fittings / extend pipes | Connect male pipes/nipples together |
| Length Range | Close to 12″+ | Usually under 3″ |
| Installation | Threads into female fittings | Male fittings thread into it |
| Space Added | Adds length to system | Minimal length addition |
| Removal | Need to unscrew from both ends | Can unscrew pipes from coupling |
| Common Uses | Extensions, fixture connections | Permanent pipe joining, repairs |
| Typical Cost | Lower (simpler manufacturing) | Slightly higher (more machining) |
When to Use Pipe Nipples
Choose pipe nipples when you need to:
- Connect two female-threaded components
- Example: Joining two ball valves, connecting a valve to an elbow
- Extend an existing pipe run
- When you need to add 2-12 inches of length
- More economical than replacing entire pipe sections
- Create spacing between fittings
- Allows room for operation of valves or access to connections
- Barrel nipples provide clearance
- Make quick, removable connections
- Can be unscrewed from one side for maintenance
- Common in accessible piping
- Connect fixtures
- Plumbing fixtures, water heaters, pressure tanks
- Close nipples for compact installations
When to Use Pipe Couplings
Choose pipe couplings when you need to:
- Join two male-threaded pipes or nipples
- Creating straight runs from shorter sections
- Repair broken pipe sections
- Make permanent connections
- Full couplings create strong, leak-resistant joints
- Often used in concealed or inaccessible locations
- Transition between pipe sizes (reducing couplings)
- Connecting 1″ pipe to 3/4″ pipe
- More compact than using bushings
- Create branch connections (half couplings)
- Socket weld to main pipe, threaded connection for branch
- Instrument and gauge connections
- Drain and vent connections
- Minimize overall system length
- Full couplings add minimal length compared to nipples
- Important in space-constrained installations
Material Considerations for Both Fittings
Both pipe nipples and couplings are available in multiple materials. Your choice depends on:
Stainless Steel (304, 316, 316L)
- Best for: Corrosive environments, food/pharma, marine applications
- Advantages: Excellent corrosion resistance, hygienic, long lifespan
- Cost: Higher initial investment
- SANVO offers: 304, 304L, 316, 316L in all standard sizes
Carbon Steel
- Best for: General industrial, oil & gas, high-pressure systems
- Advantages: High strength, economical, widely available
- Cost: Most economical option
- SANVO offers: ASTM A105, A106 Grade B
Galvanized Steel
- Best for: Outdoor installations, water systems, general plumbing
- Advantages: Corrosion protection, cost-effective, durable
- Cost: Mid-range pricing
- SANVO offers: Hot-dip galvanized for maximum protection
Brass
- Best for: Potable water, HVAC, decorative applications
- Advantages: Lead-free options, easy to install, attractive appearance
- Cost: Mid to high range
- SANVO offers: Lead-free brass for drinking water safety
Thread Type Selection: NPT, BSP, DIN
Regardless of whether you choose nipples or couplings, thread compatibility is critical:
NPT (National Pipe Tapered)
- Used in: North America (USA, Canada)
- Characteristics: 60° thread angle, 1:16 taper
- Sealing: Thread interference creates seal
- Sealant: PTFE tape or pipe dope required
BSP (British Standard Pipe)
- Used in: UK, Europe, Australia, Asia
- Types: BSPP (parallel) and BSPT (taper)
- Characteristics: 55° thread angle
- Sealing: BSPT uses thread interference; BSPP uses washer/O-ring
DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung)
- Used in: Europe, some Asian markets
- Characteristics: Metric sizing, ISO 7-1 standard
- Common in: Industrial applications, hydraulic systems
⚠️ Critical: Never mix incompatible thread types. NPT and BSP threads cannot be interchanged even if sizes appear similar.
Installation Best Practices
For Pipe Nipples:
- Select appropriate length: Measure carefully to avoid excessive length
- Check thread condition: Ensure threads are clean and undamaged
- Apply thread sealant:
- PTFE tape: 3-4 wraps clockwise (viewing thread end)
- Pipe dope: Apply to male threads only
- Hand-tighten first: Thread into both fittings by hand to ensure proper alignment
- Wrench-tighten: 2-3 turns past hand-tight (avoid overtightening)
- Use two wrenches: Hold one fitting stationary, turn the other
For Pipe Couplings:
- Full Couplings:
- Thread first pipe halfway into coupling
- Thread second pipe into opposite end
- Use wrench on coupling’s hex flats, not on pipes
- Tighten both connections evenly
- Half Couplings:
- Weld socket end first (if socket weld type)
- Allow proper cooling before threading connection
- Thread male fitting into threaded end
- Reducing Couplings:
- Determine flow direction if relevant
- Thread larger pipe first for easier alignment
- Verify size transition matches system requirements
Sizing Guide: Choosing the Right Diameter
Both nipples and couplings must match your pipe size. Common sizes and applications:
| Size | Common Applications | Flow Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ – 1/4″ | Instrument connections, gauge lines, air | Low flow |
| 3/8″ – 1/2″ | Residential plumbing, small equipment | Residential |
| 3/4″ – 1″ | General plumbing, HVAC, moderate flow | Commercial |
| 1-1/4″ – 2″ | Industrial piping, high flow applications | Industrial |
| 2-1/2″ – 6″ | Main lines, large volume transfer | High capacity |
SANVO offers all sizes from 1/8″ to 6″ with MOQ of just 50 pieces per size.
Quality Considerations When Purchasing
Whether buying nipples or couplings, verify:↳
Material Certification
- Request mill test certificates (MTC)
- Verify material grade matches specification
- Check chemical composition analysis
Dimensional Accuracy
- Thread pitch and angle must meet standards
- Wall thickness affects pressure rating
- Length tolerance (especially for nipples)
Surface Finish
- Smooth threads for proper sealing
- Galvanizing thickness (for galvanized fittings)
- Pickling and passivation (for stainless steel)
Standards Compliance
- ASME B16.11 (dimensional standards)
- ASTM material standards
- ISO, DIN, BS standards as applicable
SANVO provides: ✓ Full material traceability ✓ ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturing ✓ 100% dimensional inspection ✓ Pressure testing available ✓ Third-party inspection accepted (SGS, TUV, BV)
Pressure Ratings: What You Need to Know
Both nipples and couplings are available in different pressure classes:
Class 2000 (Standard)
- Suitable for most commercial applications
- Water, air, low-pressure steam
- Economical choice
Class 3000 (High Pressure)
- Oil & gas applications
- High-pressure steam
- Process piping
- Thicker walls, heavier construction
Class 6000 (Extra High Pressure)
- Critical oil & gas operations
- Very high-pressure systems
- Premium pricing
- Require careful installation
Important: Pressure ratings decrease with temperature. Always consult pressure-temperature charts for your specific application.
Cost Comparison and Value Analysis
Pipe Nipples
- Unit cost: Generally lower than couplings
- Installation time: Quick (thread into existing fittings)
- Best value: When extending pipes or connecting female fittings
- Bulk pricing: Significant savings on large orders
Pipe Couplings
- Unit cost: Slightly higher due to internal threading
- Installation time: Moderate (joining two pipes)
- Best value: Permanent connections, repairs, size transitions
- Half couplings: Higher cost but eliminates need for tees in some applications
Total Cost of Ownership
Consider:
- Initial purchase price
- Installation labor
- Maintenance requirements
- Longevity and replacement frequency
- System downtime during repairs
SANVO’s competitive advantage:
- Factory-direct pricing
- Low MOQ (50 pieces) for project flexibility
- Free samples for evaluation
- Volume discounts available
- Fast delivery (7-14 days standard items)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Using Wrong Thread Type
Mixing NPT and BSP will cause leaks and thread damage. ✅ Solution: Verify thread standard before ordering.
❌ Overtightening
Can split fittings or damage threads. ✅ Solution: Use torque specifications; 2-3 turns past hand-tight.
❌ Insufficient Thread Sealant
Leads to leaks and system failures. ✅ Solution: Apply adequate PTFE tape or pipe dope.
❌ Mixing Materials Improperly
Galvanic corrosion between dissimilar metals. ✅ Solution: Use compatible materials or isolation fittings.
❌ Ignoring Pressure Ratings
Can cause catastrophic failures. ✅ Solution: Match fitting class to system pressure and temperature.
❌ Using Nipples Where Couplings Are Better
Wrong fitting for the application. ✅ Solution: Understand the difference and choose appropriately.
Real-World Application Examples
Example 1: Water Treatment Plant
Scenario: Connecting 2″ stainless steel pipes in a chlorine dosing system
Solution:
- Use 316L stainless steel full couplings for permanent pipe joints
- Use 316L nipples to connect valves and instruments
- Why: Chlorine requires 316L for corrosion resistance; couplings for main runs, nipples for accessible connections
Example 2: HVAC Installation
Scenario: Residential heating system with 3/4″ and 1″ pipes
Solution:
- Galvanized nipples for fixture connections (radiators, boilers)
- Reducing couplings (1″ to 3/4″) for size transitions
- Why: Galvanized protects against condensation; nipples allow easy fixture removal; reducing couplings save space
Example 3: Oil & Gas Pipeline
Scenario: High-pressure 2″ carbon steel pipeline, Class 3000
Solution:
- Carbon steel Class 3000 couplings for permanent field joints
- Carbon steel nipples for gauge and instrument connections
- Why: High pressure requires Class 3000; couplings for main line integrity; nipples for serviceable instrument connections
Example 4: Food Processing Plant
Scenario: Dairy processing equipment, sanitary requirements
Solution:
- 304L stainless steel nipples for equipment connections
- 304L electropolished couplings for permanent piping
- Why: Food-grade stainless; 304L for weldability; electropolished for hygiene
Making Your Purchase Decision
For Pipe Nipples, Consider:
- Required length (close, shoulder, or barrel)
- Thread type compatibility
- Material for environment (corrosive, food-grade, outdoor)
- Quantity needed (SANVO MOQ: 50 pcs)
- Delivery timeframe
For Pipe Couplings, Consider:
- Type needed (full, half, or reducing)
- Pressure class requirements
- Size(s) for reducing couplings
- Socket weld vs threaded (for half couplings)
- Hex vs round body (for installation access)
Why Choose SANVO for Your Pipe Fittings
As a specialized B2B manufacturer, SANVO focuses exclusively on pipe nipples and couplings, ensuring:
Quality Assurance
✓ ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturing ✓ 100% dimensional inspection ✓ Material test certificates (MTC) provided ✓ Third-party inspection accepted
Material Options
✓ Stainless Steel: 304, 304L, 316, 316L ✓ Carbon Steel: ASTM A105, A106 Gr.B ✓ Galvanized Steel: Hot-dip galvanized ✓ Brass: Lead-free available
Thread Standards
✓ NPT (American standard) ✓ BSP (British standard) ✓ DIN (European standard) ✓ Custom threading available↳
Competitive Advantages
✓ Low MOQ: Just 50 pieces per size ✓ Free samples for evaluation ✓ Fast delivery: 7-14 days for standard items ✓ Factory-direct pricing ✓ Custom manufacturing capabilities ✓ Export experience to USA, Canada, Australia
Customer Service
✓ 24-hour quote response ✓ Technical support from engineers ✓ English-speaking sales team ✓ Clear communication throughout order process
Request Your Custom Quote Today
Whether you need pipe nipples, pipe couplings, or both, SANVO can provide the exact specifications for your project.
Get Started:
- Email us: office@pipesandfittings.com
- Specify product type (nipples/couplings)
- Material required
- Sizes and quantities
- Thread type (NPT/BSP/DIN)
- Call/WhatsApp: +86 13603173851
- Direct line to our sales team
- Instant technical support
- Quick quotations
- Request Free Sample
- Test our quality before bulk order
- Verify thread compatibility
- Check material and finish
We respond within 24 hours with detailed quotations including:
- Competitive pricing
- Material certifications
- Delivery timeline
- Technical specifications
- Free sample availability
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between pipe nipples and pipe couplings is fundamental to successful piping system design and installation. While nipples (male threads) extend and connect, couplings (female threads) join and transition. Both are essential, and choosing the right fitting for each application ensures:
- Leak-free operation
- Proper system pressure rating
- Easy maintenance access
- Long-term reliability
- Cost-effective installation
With SANVO’s comprehensive range of materials, sizes, and thread types, you’ll find the exact fittings you need for any industrial, commercial, or specialized application.
Remember:
- Nipples connect female fittings
- Couplings connect male fittings
- Match materials to environment
- Verify thread compatibility
- Follow pressure ratings
- Use proper installation techniques
Ready to order? Contact SANVO today for expert guidance and competitive pricing on your pipe fitting requirements.